What is a Wire Mesh Weaving Machine and How Does It Work?
The wire mesh weaving machine plays a crucial role in various industries. This equipment efficiently creates wire mesh products used for construction, filtration, and more. Renowned expert John Smith notes, "The innovation in wire mesh weaving machines has transformed production efficiency tremendously."
These machines utilize advanced weaving techniques to produce durable mesh. They often incorporate different materials, including stainless steel and galvanized wire. A wire mesh weaving machine not only enhances productivity but also ensures high-quality outputs. Each strand of wire is precisely interlaced, reflecting the intricate design and strength needed.
However, challenges persist in this industry. Operators must regularly maintain machinery to prevent malfunctions. Moreover, staying updated with technology is crucial for competitiveness. The world of wire mesh weaving machines is constantly evolving, necessitating ongoing training for operators and engineers alike. It’s vital to balance productivity with quality, which demands continuous reflection and improvement.
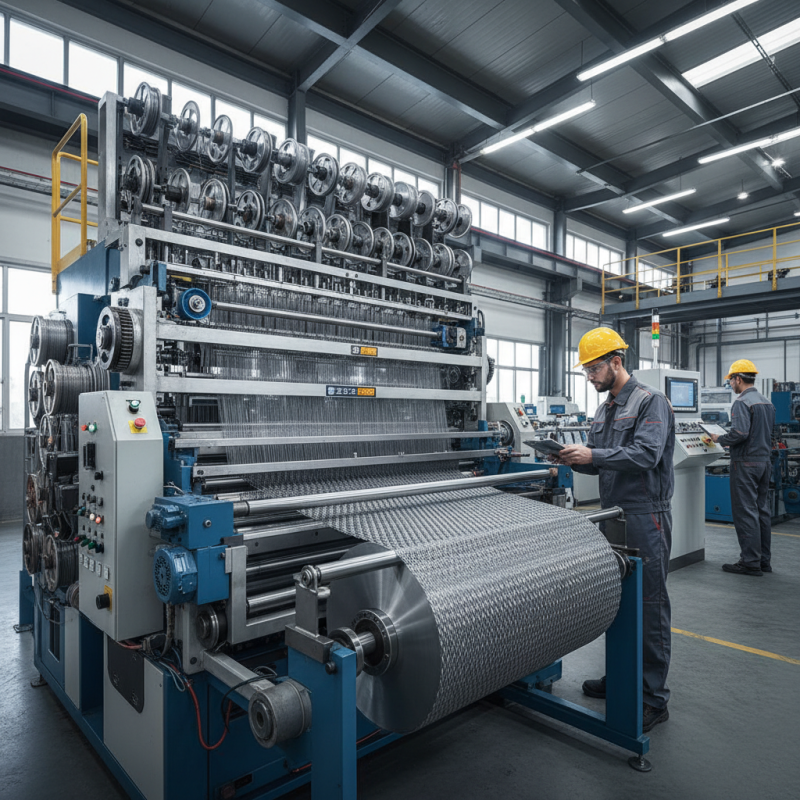

What is a Wire Mesh Weaving Machine?
A wire mesh weaving machine is essential in various industries. It creates wire mesh for construction, agriculture, and manufacturing. Different types of machines can produce various mesh sizes. Some machines weave steel, while others handle softer metals. The process can be automated or manual, depending on the intended output.
Data from the Global Wire Mesh Market Report indicates steady growth in demand. The market is projected to reach USD 4.69 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9%. This growth highlights the importance of wire mesh in industrial applications. Companies need reliable machines to keep up with this demand.
Operating a wire mesh weaving machine requires skill. It is not just about setting it up. Operators must monitor performance and make adjustments. Issues can arise, such as uneven tension or material breakage. These small problems can lead to larger failures and waste. Efficient machines are vital, yet human oversight remains crucial. Balancing technology and manual control is still a challenge in this industry.
What is a Wire Mesh Weaving Machine and How Does It Work?
| Feature | Description | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Material | Steel, stainless steel, and other materials | Used to create a durable and corrosion-resistant mesh |
| Weaving Type | Plain, twill, or specialty weaves | Determines the strength and application of the mesh |
| Machine Controls | Manual or automated systems for precision weaving | Enhances productivity and quality control |
| Production Capacity | Ranging from small-scale to industrial levels | Impacts the output scale in manufacturing |
| Applications | Construction, agriculture, filters, and safety barriers | Versatile use in various industries for different needs |
| Maintenance | Regular checks on tension and alignment | Ensures longevity and consistent performance |
Components of a Wire Mesh Weaving Machine
Wire mesh weaving machines are intricate systems designed for high efficiency and precision. Key components include the warp and weft systems that interlace wires. The warp wires are fed into the machine, held under tension. The weft wires are then woven through them, creating a strong mesh fabric. This weaving process can produce various mesh sizes and patterns, meeting diverse industrial needs.
In addition to the weaving systems, a wire mesh weaving machine consists of several crucial elements. The motor drives the entire mechanism, ensuring consistent speed. Sensors monitor the wire tension and fabric quality. Reports indicate that effective monitoring can reduce material waste by as much as 25%. Furthermore, the machine’s software controls the weaving pattern, allowing customization for specific applications. Data shows that machines with advanced software capabilities can increase production rates by up to 40%.
Despite advancements, these machines can face challenges. Maintenance is essential to prevent breakdowns, as wear can drastically affect output quality. Unsynchronized wires may cause misaligned patterns, leading to significant material loss. Reflection on these issues is vital to improve overall efficiency and adaptability in the growing wire mesh industry.
Principles of Operation for Wire Mesh Weaving Machines
Wire mesh weaving machines are crucial in various industries. These machines create a net-like structure using metal wires. They operate on simple but effective weaving principles. Two primary methods are prevalent: plain weave and twill weave. The plain weave involves over-and-under patterns, while twill weave uses diagonal patterns. Each method has distinct applications, affecting the strength and flexibility of the mesh produced.
According to industry reports, the global wire mesh market is expected to reach $6 billion by 2025, reflecting steady demand. In 2021, the growth rate of wire products was 3.5%, showcasing ongoing investments in infrastructure and construction. These data suggest a robust future for weaving technology. However, the technology still faces challenges. Machines often require frequent maintenance to avoid downtime. Operational efficiency may diminish if regular checks are neglected. Moreover, not all machines can handle high tensile strength wires, limiting their capability in demanding applications.
Weaving machines contribute uniquely to various fields, including construction, agriculture, and industrial sectors. Yet, manufacturers must address inefficiencies in their designs. Advances in automation may enhance operating speed but can also complicate repairs. Addressing these challenges is essential for sustained growth in this sector. Balancing speed and reliability remains a key focus for many industry leaders.
Types of Wire Mesh Weaving Machines Available
When exploring the world of wire mesh weaving machines, several types stand out. One common type is the automatic weaving machine. This machine can produce wire mesh efficiently. It uses electronic controls for precise operation. These machines can handle various wire sizes and materials. Their speed often leads to high production volumes.
Another prevalent type is the semi-automatic weaving machine. This machine requires some manual input for operation. It allows for flexibility in production runs. Operators can adjust settings based on specific requirements. However, this type may lead to inconsistencies without proper attention. Regular maintenance is crucial to maintaining performance.
In addition, there are specialized machines for specific applications. For example, machines designed for welded wire mesh differ significantly from traditional weaving machines. They often produce heavier and sturdier mesh. This mesh is vital for construction and safety. These specialized machines illustrate the diversity within the industry. Each type has its challenges and strengths, making selection critical.
Applications and Uses of Wire Mesh in Various Industries
Wire mesh has numerous applications across various industries. In construction, it serves as a reinforcement tool in concrete projects. According to a report from the Construction Industry Association, approximately 70% of concrete used in skyscrapers contains wire mesh. This increases durability and adds strength. The mesh holds together more effectively than traditional methods.
In agriculture, wire mesh is vital for fencing and crop protection. Reports indicate that a significant portion of farms utilizes wire mesh for safeguarding plants from pests. Almost 80% of U.S. farms employ some form of mesh to enhance yields. It provides a physical barrier while allowing sunlight and rain to penetrate, fostering healthy growth.
The automotive industry also benefits from wire mesh. It is used in air filters, improving vehicle efficiency. Research suggests that wire mesh within filters can enhance performance by 15%. However, innovation is needed to address durability issues in extreme conditions. Some mesh types wear out too quickly, affecting their applications. Balancing performance and longevity is an ongoing challenge.
Article Source:












